Spring的一个核心功能是IOC,就是将Bean初始化加载到容器中,Bean是如何加载到容器的,可以使用Spring注解方式或者Spring XML配置方式。
Spring注解方式减少了配置文件内容,更加便于管理,并且使用注解可以大大提高了开发效率!
下面按照分类讲解Spring中常用的一些注解。
主键类注解
@Component :标准一个普通的spring Bean类。
@Repository:标注一个DAO组件类。
@Service:标注一个业务逻辑组件类。
@Controller:标注一个控制器组件类。
这些都是注解在平时的开发过程中出镜率极高,@Component、@Repository、@Service、@Controller实质上属于同一类注解,用法相同,功能相同,区别在于标识组件的类型。@Component可以代替@Repository、@Service、@Controller,因为这三个注解是被@Component标注的。
举例说明
1)当一个组件代表数据访问层(DAO)的时候,我们使用@Repository进行注解,如下
1 | |
2)当一个组件代表业务层时,我们使用@Service进行注解,如下
1 | |
3)当一个组件作为前端交互的控制层,使用@Controller进行注解,如下
1 | |
总结注意点
1、被注解的java类当做Bean实例,Bean实例的名称默认是Bean类的首字母小写,其他部分不变。@Service也可以自定义Bean名称,但是必须是唯一的!
2、尽量使用对应组件注解的类替换@Component注解,在spring未来的版本中,@Controller,@Service,@Repository会携带更多语义。并且便于开发和维护!
3、指定了某些类可作为Spring Bean类使用后,最好还需要让spring搜索指定路径,在Spring配置文件加入如下配置:
1 | |
装配bean时常用的注解
@Autowired:属于Springorg.springframework.beans.factory.
annotation包下,可用于为类的属性、构造器、方法进行注值
@Resource:不属于spring的注解,而是来自于JSR-250位于java.annotation包下,使用该annotation为目标bean指定协作者Bean。
@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 方法 实现初始化和销毁bean之前进行的操作
举例说明
1):@Autowired
源码1
2
3
4
5
6@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
boolean required() default true;
}
实例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10@Controller
public class HappyController {
@Autowired //默认依赖的ClubDao 对象(Bean)必须存在
//@Autowired(required = false) 改变默认方式
@Qualifier("goodClubService")
private ClubService clubService;
// Control the people entering the Club
// do something
}
2):@Resource
源码1
2
3
4
5
6@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Resource {
String name() default "";
Class type() default java.lang.Object.class;
...
实例
1 | |
总结
1):相同点
@Resource的作用相当于@Autowired,均可标注在字段或属性的setter方法上。
2):不同点
a:提供方 @Autowired是Spring的注解,@Resource是javax.annotation注解,而是来自于JSR-250,J2EE提供,需要JDK1.6及以上。
b :注入方式 @Autowired只按照Type 注入;@Resource默认按Name自动注入,也提供按照Type 注入;
c:属性
@Autowired注解可用于为类的属性、构造器、方法进行注值。默认情况下,其依赖的对象必须存在(bean可用),如果需要改变这种默认方式,可以设置其required属性为false。
还有一个比较重要的点就是,@Autowired注解默认按照类型装配,如果容器中包含多个同一类型的Bean,那么启动容器时会报找不到指定类型bean的异常,解决办法是结合@Qualified注解进行限定,指定注入的bean名称。
@Resource有两个中重要的属性:name和type。name属性指定byName,如果没有指定name属性,当注解标注在字段上,即默认取字段的名称作为bean名称寻找依赖对象,当注解标注在属性的setter方法上,即默认取属性名作为bean名称寻找依赖对象。
需要注意的是,@Resource如果没有指定name属性,并且按照默认的名称仍然找不到依赖对象时, @Resource注解会回退到按类型装配。但一旦指定了name属性,就只能按名称装配了。
d:@Resource注解的使用性更为灵活,可指定名称,也可以指定类型 ;@Autowired注解进行装配容易抛出异常,特别是装配的bean类型有多个的时候,而解决的办法是需要在增加@Qualitied进行限定。
Spring中 @Autowired注解与@Resource注解的区别
注意点:使用@Resource也要注意添加配置文件到Spring,如果没有配置component-scan
1 | |
则一定要配置 annotation-config
1 | |
@Component vs @Configuration and @Bean
简单介绍
Spring的官方团队说@Component可以替代 @Configuration注解,事实上我们看源码也可以发现看到,如下
1 | |
虽然说可以替代但是两个注解之间还是有区别的!
Bean注解主要用于方法上,有点类似于工厂方法,当使用了@Bean注解,我们可以连续使用多种定义bean时用到的注解,譬如用@Qualifier注解定义工厂方法的名称,用@Scope注解定义该bean的作用域范围,譬如是singleton还是prototype等。
Spring 中新的 Java 配置支持的核心就是@Configuration 注解的类。这些类主要包括 @Bean 注解的方法来为 Spring 的 IoC 容器管理的对象定义实例,配置和初始化逻辑。
使用@Configuration 来注解类表示类可以被 Spring 的 IoC 容器所使用,作为 bean 定义的资源。
1 | |
这和 Spring 的 XML 文件中的非常类似
1 | |
@Bean 注解扮演了和元素相同的角色。
举例说明@Component 和 @Configuration
1 | |
@Component
public static class Config {
@Bean
public SimpleBean simpleBean() {
return new SimpleBean();
}
@Bean
public SimpleBeanConsumer simpleBeanConsumer() {
return new SimpleBeanConsumer(simpleBean());
}
}
第一个代码正常工作,正如预期的那样,SimpleBeanConsumer将会得到一个单例SimpleBean的链接。第二个配置是完全错误的,因为Spring会创建一个SimpleBean的单例bean,但是SimpleBeanConsumer将获得另一个SimpleBean实例(也就是相当于直接调用new SimpleBean() ,这个bean是不归Spring管理的),既new SimpleBean() 实例是Spring上下文控件之外的。
总结
使用@ configuration,所有标记为@ bean的方法将被包装成一个CGLIB包装器,它的工作方式就好像是这个方法的第一个调用,那么原始方法的主体将被执行,最终的对象将在spring上下文中注册。所有进一步的调用只返回从上下文检索的bean。
在上面的第二个代码块中,新的SimpleBeanConsumer(simpleBean())只调用一个纯java方法。为了纠正第二个代码块,我们可以这样做
1 | |
Spring @Configuration vs @Component
基本概念:@Configuration 和@Bean
spring MVC模块注解
web模块常用到的注解
@Controller :表明该类会作为与前端作交互的控制层组件,通过服务接口定义的提供访问应用程序的一种行为,解释用户的输入,将其转换成一个模型然后将试图呈献给用户。
1 | |
Spring MVC 使用 @Controller 定义控制器,它还允许自动检测定义在类路径下的组件(配置文件中配置扫描路径)并自动注册。
@RequestMapping : 这个注解用于将url映射到整个处理类或者特定的处理请求的方法。可以只用通配符!
1 | |
@RequestMapping 既可以作用在类级别,也可以作用在方法级别。当它定义在类级别时,标明该控制器处理所有的请求都被映射到 /favsoft 路径下。@RequestMapping中可以使用 method 属性标记其所接受的方法类型,如果不指定方法类型的话,可以使用 HTTP GET/POST 方法请求数据,但是一旦指定方法类型,就只能使用该类型获取数据。
@RequestParam :将请求的参数绑定到方法中的参数上,有required参数,默认情况下,required=true,也就是改参数必须要传。如果改参数可以传可不传,可以配置required=false。
1 | |
@PathVariable : 该注解用于方法修饰方法参数,会将修饰的方法参数变为可供使用的uri变量(可用于动态绑定)。
1 | |
@PathVariable中的参数可以是任意的简单类型,如int, long, Date等等。Spring会自动将其转换成合适的类型或者抛出 TypeMismatchException异常。当然,我们也可以注册支持额外的数据类型。
@PathVariable支持使用正则表达式,这就决定了它的超强大属性,它能在路径模板中使用占位符,可以设定特定的前缀匹配,后缀匹配等自定义格式。
1 | |
//可以绑定自定义的对象类型
}
@ResponseBody : @ResponseBody与@RequestBody类似,它的作用是将返回类型直接输入到HTTP response body中。
@ResponseBody在输出JSON格式的数据时,会经常用到。
1 | |
@RestController :控制器实现了REST的API,只为服务于JSON,XML或其它自定义的类型内容,@RestController用来创建REST类型的控制器,与@Controller类型。@RestController就是这样一种类型,它避免了你重复的写@RequestMapping与@ResponseBody。
@ModelAttribute :@ModelAttribute可以作用在方法或方法参数上,当它作用在方法上时,标明该方法的目的是添加一个或多个模型属性(model attributes)。
该方法支持与@RequestMapping一样的参数类型,但并不能直接映射成请求。控制器中的@ModelAttribute方法会在@RequestMapping方法调用之前而调用。
@ModelAttribute方法有两种风格:一种是添加隐形属性并返回它。另一种是该方法接受一个模型并添加任意数量的模型属性。用户可以根据自己的需要选择对应的风格。
Spring事务模块注解
1、常用到的注解
在处理dao层或service层的事务操作时,譬如删除失败时的回滚操作。使用@Transactional 作为注解,但是需要在配置文件激活
1 | |
2、举例
1 | |
总结
事务的传播机制和隔离机制比较重要!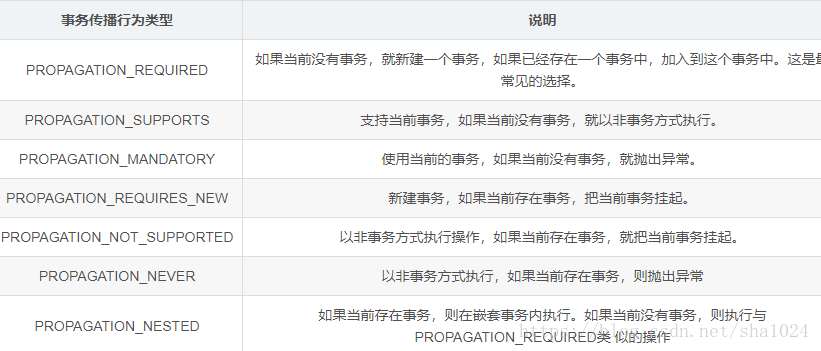 )
)
readOnly : 事务的读写属性,取true或者false,true为只读、默认为false
rollbackFor : 回滚策略,当遇到指定异常时回滚。譬如上例遇到异常就回滚
timeout (补充的) : 设置超时时间,单位为秒
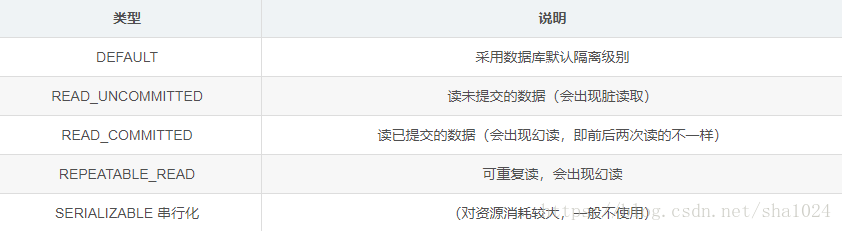
isolation : 设置事务隔离级别,枚举类型,一共五种
透彻的掌握 Spring 中@transactional 的使用